Steller Sea Lion
(Eumetopias jubatus)
Printer Friendly
Did You Know?
Steller sea lions occupy over 300 haulouts from Japan to California.
General Description
The Steller (or northern) sea lion (Eumetopias jubatus) is the largest member of the family Otariidae, the “eared seals,” which includes all sea lions and fur seals. It is the only member of genus Eumetopias. Otariids differ from phocids, the “true seals,” in having external ear flaps, long forearms resembling flippers used for propulsion, and rotatable hind flippers that allow quadrupedal locomotion on land.
At birth, pups have dense, coarse, nearly black fur with a frosty appearance because the tips of the hair are colorless. Color lightens after their first molt in late summer. Most adult females are buff colored on the back. Nearly all males stay darker on the front of the neck and chest; some are even a reddish color. Adult males have prominent, broad foreheads and muscular necks. The sound of a Steller sea lion haulout is a chorus of low-pitched “roars” of older individuals mixed with the “lamb-like” vocalizations of young pups. California sea lions may often be heard among Steller sea lions in southeastern Alaska haulouts; their “barking” sounds are a distinctive cue to look for these smaller, darker sea lions.
Steller sea lions are known to several languages: in Aleut, qawax; in Alutiiq, wiinaq; in Central Yup’ik, uginaq (sometimes apakcuk) and in Siberian Yup’ik, ulgaq. The Russian common name translates to “sea wolf.” Eumetopias, from the Greek, means “having a broad forehead”, and jubatus, from Latin, means “having a mane.”
Life History
Reproduction and Growth
Males may live up to 20 years and females to 30 years. Males reach sexual maturity at 3-7 years but do not hold territories on breeding rookeries until 9-13 years. Females start breeding at 3-7 years and spend the next two decades either pregnant or lactating. Females are bred in June, but the fertilized egg does not implant until October. Single pups are born the following June, with birthdates at southern rookeries earlier than births at northern rookeries. Twins are rare. Pups suckle from 1 to 3 years, with most apparently weaning after their first winter.
Males and females have a marked size difference. Weight at birth is 51 pounds (23 kg), and body length is 45 inches (112 cm). Females grow rapidly during the first four years but slow by the fifth year, with little growth after age 6. Males continue to grow until the eleventh year. Although there are variations, most females reach maximum size by the seventh year, and males reach adult size by the twelfth year. The average weight of an adult male is 1,245 pounds (566 kg), and the body length averages 10’ 8” (282 cm). Adult females average 579 pounds (263 kg) in weight and 8’ 8” (228 cm) in length. Although only 20 percent longer, the average adult male weighs over twice as much as the average adult female.
Feeding Ecology
Scientists use kitchen spoons to scrape sea lion scat off rocky haulouts throughout Alaska and Canada. This scat is examined for the presence of “hard parts,” such as fish bones or squid beaks, that can be keyed to prey species eaten by sea lions. Recently, scientists are also attempting to identify the chemical signatures of prey items in the blood and blubber of sea lions.
From this work we know that Steller sea lions are generalist marine predators with a diet of fishes and cephalopods that tends to be predictable by season and region, with the occasional meal of bird or true seal for variety. Some prey are generally available year-round, such as walleye Pollock, Atka mackerel, arrowtooth flounder and cephalopods, while others are targeted by sea lions when they become seasonally abundant, such as Pacific herring, Pacific salmon, Pacific cod, eulachon and capelin. Western Alaska diets are dominated by Atka mackerel and walleye pollock and eastern diets feature walleye pollock, Pacific cod, flatfish, rockfish and forage fish. Sea lions can consume prey whole while underwater.
Migration
Sea lions do not migrate, but do move their “central-place haulout,” the center of their foraging activity, to track seasonal concentrations of their many types of prey. They breed on exposed, offshore rookeries during summer and generally move to more protected haulouts in winter, especially in southeastern Alaska. Very young sea lions can swim 75 miles (120 km) non-stop between haulouts. Some sea lions make long-distance movements over long periods of time. The longest recorded movements are Forrester Island to Cape Newenham (1,600 miles / 2,500 km), Kozlof Cape, Russia to Round Island (1,400 miles / 2,300 km) and Medny Island, Russia to Round Island (1,200 miles / 2,000 km).
Behavior
Steller sea lions use rookeries and haulouts on land to rest and suckle their young. Adult females must continue foraging while nursing their pups, and the pups’ bodies are well-adapted to fast while females are hunting prey during 1-2 day trips. By their first spring, pups are able to reach similar diving depths as adults but do not do so as frequently. As pups grow older, their swimming and diving patterns grow to resemble that of older sea lions. The behavior of older juveniles and adults appears to track the behavior of their prey; for example, deep diving as prey move deeper during daylight, a focus on night-time behavior while prey are shallow and the gathering of many sea lions at places with seasonal runs of forage fish. Foraging trips are usually within a few tens of miles off haulouts, but the longest recorded continuous foraging trip was 550 miles (900 km) into the Bering Sea. Older juvenile sea lions can dive to at least 1500 feet (500 meters) and stay underwater for over 16 minutes. When swimming, Steller sea lions use their front flippers for propulsion and their back flippers to steer. When moving on land, they use a “rolling walk” on all four flippers by pulling their hind flippers under their body. Steller sea lions are capable climbers, often found high above the water on cliff faces.
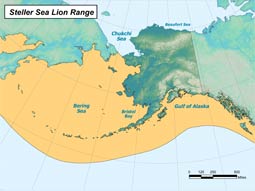
Range and Habitat
Steller sea lions inhabit over 300 haulouts and rookeries along the North Pacific rim from Hokkaido, Japan, north along the Kuril Islands into Kamchatka and the Sea of Okhotsk, east along the Aleutian chain and into the central Bering Sea, through the Gulf of Alaska, south through southeastern Alaska, the Canadian Pacific coast and to the Channel Islands off California. Steller sea lion females exhibit high site fidelity, generally using the same rookeries to breed and birth their pups each year. These sites are usually on remote islands where access by predators is limited.
Status, Trends, and Threats
Status
In 1990, Steller sea lions were listed as “threatened” range-wide under the Endangered Species Act of 1973 due to the dramatic population decline in the western portion of their range. Meanwhile, scientists identified substantial genetic differences, regional differences in population trend and a low exchange rate of breeding animals between rookeries, indicating that Steller sea lions existed in “distinct population segments.” Thus, in 1997, the population was split immediately east of Cape Suckling on the Gulf of Alaska coast (near 144º W longitude) into an “endangered” Western Stock and “threatened” Eastern Stock. The threatened Eastern Stock was delisted in 2013. To learn more, visit the ADF&G Special Status page for Steller sea lion.
Trends
During the late 20th century, the western Alaska Steller sea lion population (the Gulf of Alaska and Aleutian Islands) suffered a substantial decline, but there are signs of stabilization in recent years. The first population trend counts made in 1956-1960 estimated at least 140,000 sea lions in this area. A major population decrease was first detected in the eastern Aleutians during the mid-1970s and the estimated population dropped to 110,000 by the late 1970s. The decline spread eastward into the Kodiak Archipelago during the late 1970s and early 1980s, then spread westward through the Aleutian Islands during the early to mid-1980s, with the steepest declines of 15% per year occurring during the late 1980s. By 1990 the population was 30,525, and decline continued through the 1990s at 5.4% per year. Between 2000 and 2004, surveys found increasing or stable numbers throughout the Western Stock. Meanwhile, the Eastern Stock has increased by over 3% per year since the 1970s, and likely exceeded 50,000 animals in 2007. Indeed, new breeding rookeries have become established in southeastern Alaska in the early 21st century.
At the turn of the 21st century, there is substantial effort being made to identify causes for and remedies to the Western stock population decline, and these are the subject of considerable debate. The possible sources of the decline being examined are grouped into “top-down” processes, such as predation, disturbance, intentional killing and entanglements, and “bottom-up” processes, such as reduced prey quality or abundance and long-term shifts in their environment. Assessment of these threats and planning for the recovery of Steller sea lions is a long-term collaborative process involving numerous stakeholder groups. One-fifth of one percent of Steller sea lions sighted during surveys in southeastern Alaska are entangled by marine debris including packing straps and fishing gear, but the extent of mortality due to this is unknown.
Fast Facts
-
Size
579 pounds for females, 1,245 pounds for males -
Lifespan
20–30 years -
Distribution/Range
North Pacific Ocean from Japan to California, including Bering Sea -
Diet
Fish and cephalopods -
Predators
Killer whales, sharks -
Reproduction
Colonial breeder that gives birth to one pup a year -
Other names
Northern sea lion
Did You Know?
- Steller sea lions occupy over 300 haulouts from Japan to California.
- Adult male sea lions are 650 pounds heavier than adult females on average.
- Sea lion pups suckle from 1 to 3 years.
- The longest recorded movement of a Steller sea lion was 1,600 miles between Forrester Island in Southeast and Cape Newenham in Bristol Bay.
- Steller sea lions can dive over 1,500 feet deep and stay underwater for 16 minutes.
- Steller sea lions are the largest sea lion in the world.
- Female Steller sea lions use smell and sound to recognize their pups.
- Sea lions get their name because the males have long, thick hair on their head and neck resembling a mane.
Uses
Historically, Steller sea lions were used as a food source, clothing, boat coverings, meat for fox farms and craftwork. The commercial pup harvest in 1964-1972 provided fur for clothing manufacture. Contemporary use includes food, some clothing and craftwork. While the Steller sea lion population is listed as “depleted” under the Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972, and thus subsistence takes are subject to Federal management, subsistence harvest continues because it has not been shown to contribute to the decline. Between 2000-2004, 191 were taken per year in the Western stock, and 6 per year in the East.
Management
 Steller sea lions are managed by the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), a branch of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Administration. The species falls under the jurisdiction of the Marine Mammal Protection Act and is protected under the
Endangered Species Act. Comanagement agreements have been established between the NMFS and the Aleut Marine Mammal Commission,
the Traditional Council of St George Island and the Traditional Council of St Paul Island.
Steller sea lions are managed by the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), a branch of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Administration. The species falls under the jurisdiction of the Marine Mammal Protection Act and is protected under the
Endangered Species Act. Comanagement agreements have been established between the NMFS and the Aleut Marine Mammal Commission,
the Traditional Council of St George Island and the Traditional Council of St Paul Island.
Additionally, NMFS has enacted regulations to reduce threats to Steller sea lions including prohibitions on shooting at or near sea lions by anyone other than Alaska Native subsistence hunters, no-entry zones for vessels around rookeries, limits on incidental take of sea lions in commercial fisheries and research, and fishery closures in the waters surrounding some rookeries.
Complete information about Steller sea lion management may be found at the NMFS Alaska Regional Office.
Research
 The ADF&G Steller Sea Lion Program supports recovery of Steller sea lions in Alaska through extensive field and laboratory
research. We have studied sea lions from the 1970’s to the present. Currently our research is designed to understand the factors
impeding recovery of the western population of Steller sea lions, and then compare them to our studies of the eastern population
that continues to increase. Learn more at the Steller Sea Lion Program website.
The ADF&G Steller Sea Lion Program supports recovery of Steller sea lions in Alaska through extensive field and laboratory
research. We have studied sea lions from the 1970’s to the present. Currently our research is designed to understand the factors
impeding recovery of the western population of Steller sea lions, and then compare them to our studies of the eastern population
that continues to increase. Learn more at the Steller Sea Lion Program website.
Get Involved
Report an Injured or Dead Sea Lion
Report your sightings of injured or dead sea lions to the National Marine Fisheries Service Alaska 24 hr Stranding Hotline: (877) 925-7773 or (877) 9-AKR-PRD. Sea lion carcasses provide valuable biological information if biologists can reach them quickly.
Lose the Loop!
 Learn about Steller sea lion entanglement and ADF&G research to
help find ways to reduce injury and mortality from marine debris.
Learn about Steller sea lion entanglement and ADF&G research to
help find ways to reduce injury and mortality from marine debris.
Report Your Sighting of a Marked Steller Sea Lion!
Learn how ADF&G uses re-sightings of marked sea lions to learn the individual survival and reproductive rates that drive population change.
Participate in the Public Process!
Regulations affecting Steller sea lions and fisheries are enacted after public process. Learn what is under consideration and how to add your input at the NOAA Steller sea lion website.
More Resources
General Information
- Steller Sea Lion — Wildlife Notebook Series (PDF 64 kB)
- Steller Sea Lion Research — ADF&G Marine Mammal Program
- Steller Sea Lion Management, Regulation and Viewing Guidelines
- Marine Mammal Comanagement Agreements
- The Alaska Sea Otter and Steller Sea Lion Commission
Special Status Information
- Policy Actions
- Pertinent Documents
- Endangered Species Act Consultations
- Recovery Plan for the Steller Sea Lion (Revised 2008)