North Pacific Right Whale
(Eubalaena japonica)
Species Profile
Did You Know?
Right whales consume some of the smallest prey and have some of the longest baleen, up to 8 feet, of any baleen whale (Baleen whales are filter feeds and do not have teeth).
Special Status Listing: Yes, see Status, Trends and Threats.
General Description
The North Pacific right whale is a large baleen whale. Baleen whales are characterized by having baleen plates for filtering food from water, rather than having teeth. The females are larger than the males and can grow up to 55 feet. The North Pacific right whale has a very large head, approximately one-quarter of its body length, with strongly arched jaws. There are light, wart-like spots on its head called callosities. It has a wide body, lacks a dorsal fin, and is mostly black with some white patches on its underside. Right whales weigh up to 2,000 lb at birth and up to 220,000 lb at maturity, with a life span over 50 years. Two populations, or stocks, of North Pacific right whales are currently recognized one in the western North Pacific off Russia and the other in the eastern North Pacific off Alaska.
Right whales are sometimes confused with bowhead whales. Right whales typically have the obvious wart-like callosities on their heads, while the skin of bowhead whales is usually smooth. The North Pacific right whale is one of the rarest marine mammal species in the world due to heavy exploitation by commercial whalers prior to 1949.
Similar Species
The North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) and southern right whale (Eubalaena australis) are other species of right whale. The geographic ranges of the three different species of right whales do not overlap, so they never meet in their ocean travels. All species of right whales are endangered and internationally protected from whaling since 1949.
Life History
Reproduction and Growth
Female right whales generally give birth to their first calf at 9-10 years of age. Pregnancy lasts approximately 1 year. The calf is 13-15 feet and weighs up to 2,000 lb at birth and will nurse for a year. Mature right whales grow to 45-55 feet and up to 220,000 pounds (100 metric tons). Populations of right whales grow slowly because it takes a long time for female right whales to reach sexual maturity and only give birth to a single calf.
Foraging Ecology
North Pacific right whales consume zooplankton, tiny animals floating in the water column (e.g., copepods and krill), by using a technique called "skimming." With mouths open, they swim through patches of zooplankton, catching the tiny animals on their baleen. Baleen is a comb-like filtering structure made out of the same substance as hair and nails (the protein keratin). Most feeding is believed to occur between spring and fall.
Migration
The migration patterns of the North Pacific right whale are unknown. It is believed that they feed during the summer in high latitudes and move to more temperate areas for the winter.
Review of more than 3,600 North Pacific right whale calls detected by passive listening devices between 2000–2006 strongly suggests that the whales migrate into the southeast Bering Sea in late spring and remain until late fall. The earliest calls were heard in late May and the latest in December. The peak calling period was July through October. Most calls were detected from shallow waters over the continental shelf, sites within the designated Critical Habitat area encompassing the southeastern Bering Sea and Gulf of Alaska.
Behavior
Right whales spend most of their lives underwater. We gain clues about their sub-surface behavior from underwater microphones (hydrophones), data tags, and from whale dive times. Right whales have been seen returning to the surface with mud on their heads, indicating they swam to the ocean’s bottom during a dive.
At the surface, right whales exhibit a variety of behaviors:
- breaching (jumping out of the water)
- fluking (lifting the tail out of the water)
- nursing
- spy hopping (lifting the head out of the water)
- logging (resting)
- skim feeding (feeding at or just below the water’s surface)
- posturing (arching its back bringing both flukes and head out of the water)
- surface active group behavior (two or more whales socializing at the surface).
The first five behaviors are exhibited by many whale species; the last three are less common.
Range and Habitat
Whaling records indicate that right whales were once abundant throughout the eastern North Pacific and Bering Sea during the summer months in the 19th and early 20th centuries. As a result of international protection from hunting in 1935, the right whale population was growing by 1960, although large illegal catches by Soviet whalers during the 1960s in the eastern North Pacific and Bering Sea crippled recovery. The right whales in the eastern North Pacific are only a remnant of the former population and may not fully occupy the same range they did two centuries ago. While the importance of other historical habitats in the eastern North Pacific is unknown, modern sightings of right whales have led to areas of the southeastern Bering Sea and Gulf of Alaska being designated as critical habitat for North Pacific right whales.
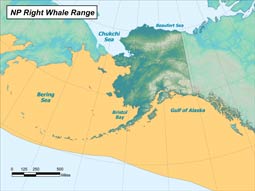
The North Pacific right whale is distributed from Baja California to the Bering Sea with the highest concentrations in the Bering Sea, Gulf of Alaska, Okhotsk Sea, Kuril Islands, and Kamchatka area. They are primarily found in coastal or shelf waters but sometimes travel into deeper waters. In the spring through the fall their distribution is dictated by the distribution of their prey. In the winter, pregnant females move to shallow waters in low latitudes to calve; the winter habitat of the rest of the population is unknown.
Alaska Focus
Heavily impacted by whaling, the eastern population of whales that occur off the west coast of Alaska currently has an abundance of only a few tens of animals, making it the most endangered marine mammal population in U.S. waters.
Between the late 1960s and the mid-1990s sightings of right whales in the eastern North Pacific were rare, widely scattered, and almost always involved solitary animals.
Significant sightings occurred in the summer of 1997 when a group of four animals was reported in the southeastern Bering Sea and in 2002 with the first confirmed sighting of a calf in decades. In 2004 a concentration of whales was found that included a minimum of 17 whales. Additionally, a whale which is thought to be a sub-adult animal was observed in Uganik Bay, Alaska in December 2011, being the first modern record of the species on the western side of Kodiak Island and one of the few sightings that has occurred in near-shore waters.
Detections of right whales have been very rare in the Gulf of Alaska, even though large numbers of whales were caught there in the 1800s. From 2004 to 2006, four sightings occurred in the Barnabus Trough region on Albatross Bank, south of Kodiak Island. This area represents important habitat for the relic population of North Pacific right whales, and a portion of this area was designated as critical habitat under the US Endangered Species Act. For a map of the North Pacific Right Whale Critical Habitat area established in 2006 and 2008, visit http://www.nmfs.noaa.gov/pr/pdfs/criticalhabitat/northpacificrightwhale.pdf.
Read more about specific sightings and locations of right whales in Alaska in the NMFS Alaska stock assessment records: http://www.nmfs.noaa.gov/pr/sars/species.htm.
NOAA Fisheries continues to conduct research on the North Pacific right whale to learn more about its population status.
2021 update: According to National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration scientists, there are about 30 members of the Eastern Group of North Pacific right whales left in the wild. In August 2021, survey vessels encountered two different pairs of right whales, each with two different individuals. Federal biologists were conducting a survey to get distribution density and abundance estimation for large whale species in the Kodiak area. Two survey vessels encountered two different pairs of right whales. Both sightings occurred near Kodiak Island, with the first sighting being on the morning of Aug. 21 around the Barnabas Trough west of Kodiak Island. The second sighting was on the Aug. 24, near the Trinity Islands on the west end of Kodiak. Two of the four whales spotted were completely new individuals, that until then had never been logged by researchers. The other two animals are known to biologists — one was seen nearby in 2006 and the other had been seen earlier this year off the coast of British Columbia.
Status, Trends, and Threats
Status
An accurate estimate of the current abundance of the North Pacific right whale is not available, although the number of whales in the eastern population is considered to be in the 10s of animals. A reliable estimate of the number of whales in the western population is not available. The species is currently listed as endangered under the Endangered Species Act (ESA). To learn more, visit the ADF&G Special Status page for North Pacific right whale.
NatureServe: Global – G1 (Critically imperiled), State – S1 (Critically imperiled)
IUCN: Endangered
U.S. (or Federal) ESA: Endangered
State of Alaska Endangered Species Policy: Endangered
Trends
The current population trend is unknown. Over 11,000 individuals likely occupied the North Pacific prior to whaling.
Threats
Threats to the North Pacific right whale potentially include inbreeding depression and low population density effects, collisions with ships and entanglement in fishing gear, pollution, degradation of feeding habitat (e.g., through effects of pollution of zooplankton), human disturbance (e.g., ships and other underwater noisemakers) and climate change and resultant changes in food supply. The potential impact on right whales, and other listed species, from proposed oil and gas development in the North Aleutian Basin should be monitored carefully; including seismic surveys conducted during the early stages of development.
Fast Facts
-
Size
Length 45-55 ft., weight at birth up to 2,000 lb, weight at maturity up to 220,000 lb -
Lifespan
At least 50 years -
Range/Distribution
Baja California to the Bering Sea concentrated in higher latitudes. -
Diet
Zooplankton -
Predators
Killer whales -
Reproduction
1 calf at a time after 9-10 years of age -
Remarks
The eastern North Pacific right whale population found off Alaska in summer is the most endangered of all large whales. A significant sighting occurred in the southeastern Bering Sea off Alaska in 1996 when a group of four whales were reported; the most North Pacific right whales seen together in almost 30 years. In 2004 an astonishing concentration of whales was found that included a minimum of 17 whales. -
Read more:
http://www.nmfs.noaa.gov/pr/pdfs/sars/ak2009whnr-pen.pdf